|
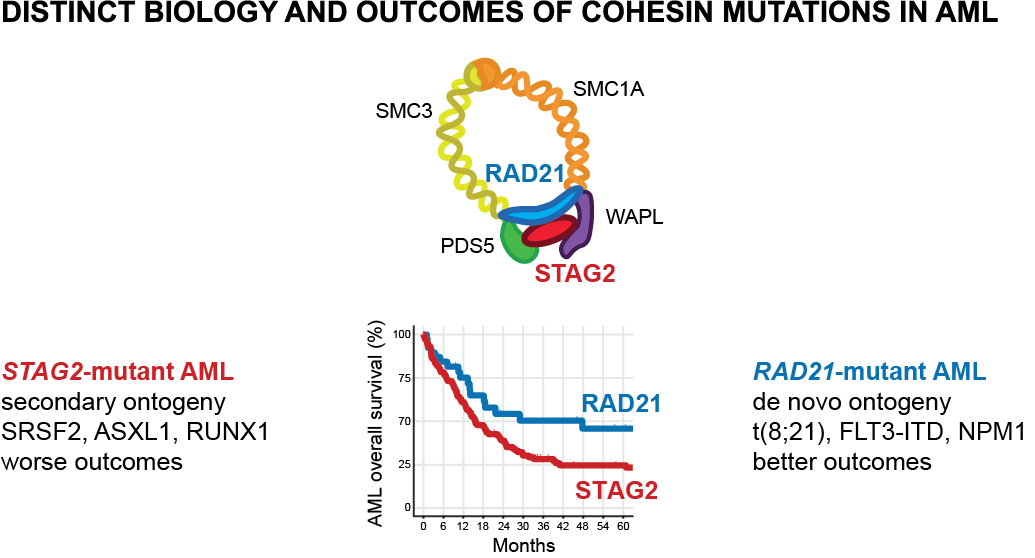
Subunit-specific analysis of cohesin-mutant myeloid malignancies reveals distinct ontogeny and outcomes
Leukemia. 2024. July 20; published online; link Mutations in the cohesin complex components (STAG2, RAD21, SMC1A, SMC3, and PDS5B) are recurrent genetic drivers in myelodysplastic neoplasm (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Whether the different cohesin subunit mutations share clinical characteristics and prognostic significance is not known. We analyzed 790 cohesin-mutant patients from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) and the Munich Leukemia Laboratory (MLL), 390 of which had available outcome data, and identified subunit-specific clinical, prognostic, and genetic characteristics suggestive of distinct ontogenies. We found that STAG2 mutations are acquired at MDS stage and are associated with secondary AML, adverse prognosis, and co-occurrence of secondary AML-type mutations. In contrast, mutations in RAD21, SMC1A and SMC3 share features with de novo AML with better prognosis, and co-occurrence with de novo AML-type lesions. The findings show the heterogeneous nature of cohesin complex mutations, and inform clinical and prognostic classification, as well as distinct biology of the cohesin complex. |
|
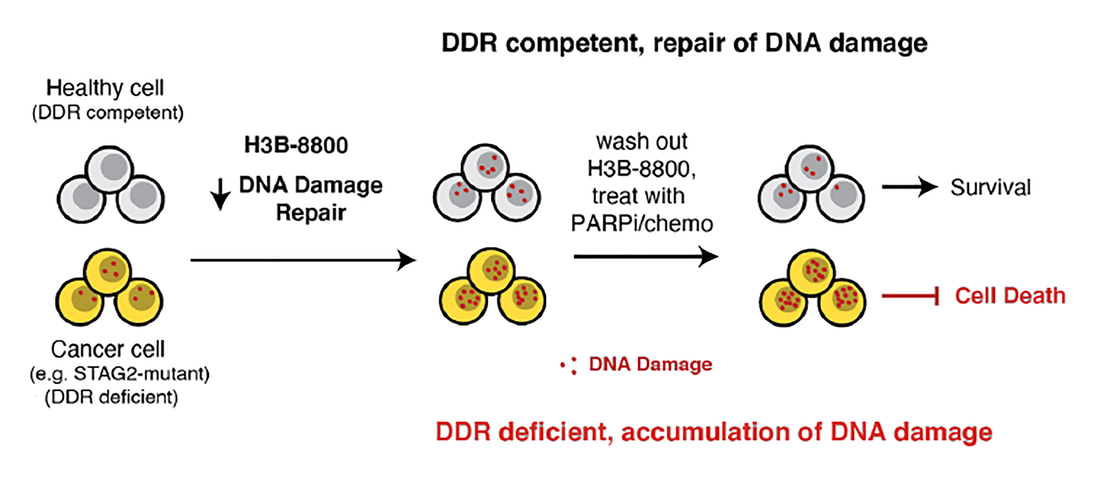
Splicing modulators impair DNA damage response and induce killing of cohesin-mutant MDS/AML
Science Translational Medicine. 2024. Jan 4; 16 (728); link Splicing modulation is a promising treatment strategy pursued to date only in splicing-factor mutant cancers; however, its therapeutic potential is poorly understood outside of this context. Like splicing factors, genes encoding components of the cohesin complex are frequently mutated in cancer, including myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where they are associated with poor outcomes. Here, we show that cohesin mutations are biomarkers of sensitivity to drugs targeting the splicing-factor SF3B1 (H3B-8800 and E-7107). We identify drug-induced alterations in splicing and corresponding reduced gene expression of a large number of DNA repair genes, including BRCA1 and BRCA2, as the mechanism underlying this sensitivity in cell line models, primary patient samples and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models of AML. We find that DNA damage repair genes are particularly sensitive to exon skipping induced by SF3B1 modulators given their long length and large number of exons per transcript. Furthermore, we demonstrate that treatment of cohesin-mutant cells with SF3B1 modulators not only results in impaired DNA damage response and accumulation of DNA damage, but it significantly sensitizes cells to subsequent killing by PARP inhibitors and chemotherapy, and leads to improved overall survival of PDX models of cohesin-mutant AML in vivo. Our findings expand the potential therapeutic benefits of SF3B1 splicing modulators to include cohesin-mutant MDS and AML, and we propose this as a broader strategy for therapeutic targeting of other DNA damage-repair deficient cancers. |
|
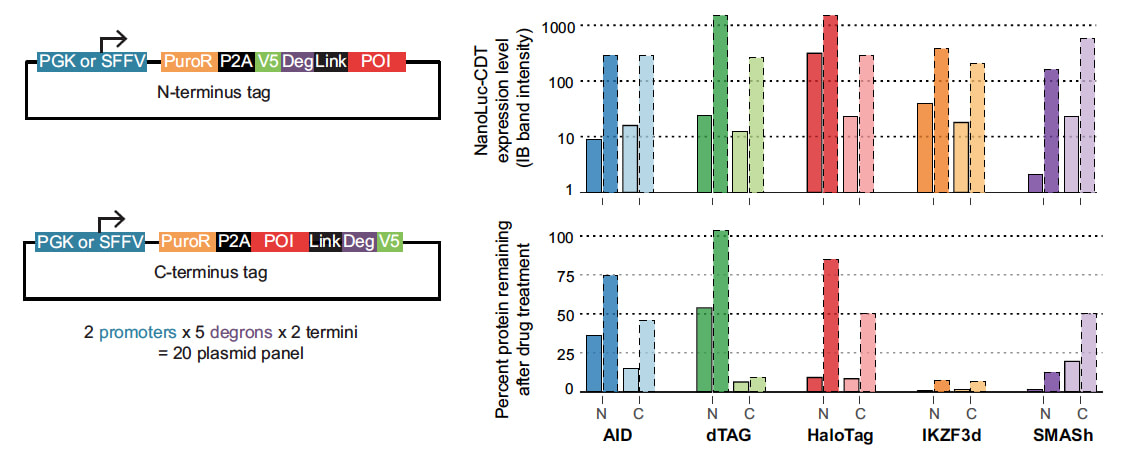
Systematic profiling of conditional degron tag technologies for target validation studies.
Nature Communications. 2022 Sep 20 (online): https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33246-4. Conditional degron tags (CDTs) are a powerful tool for target validation that combines the kinetics and reversible action of pharmacological agents with the generalizability of genetic manipulation. However, successful design of a CDT fusion protein often requires a prolonged, ad hoc cycle of construct design, failure, and re-design. To address this limitation, we report here a system to rapidly compare the activity of five unique CDTs: AID/AID2, IKZF3d, dTAG, HaloTag, and SMASh. We demonstrate the utility of this system against 16 unique protein targets. We find that expression and degradation are highly dependent on the specific CDT, the construct design, and the target. None of the CDTs leads to efficient expression and/or degradation across all targets; however, our systematic approach enables the identification of at least one optimal CDT fusion for each target. To enable the adoption of CDT strategies more broadly, we have made these reagents, and a detailed protocol, available as a community resource. |
|
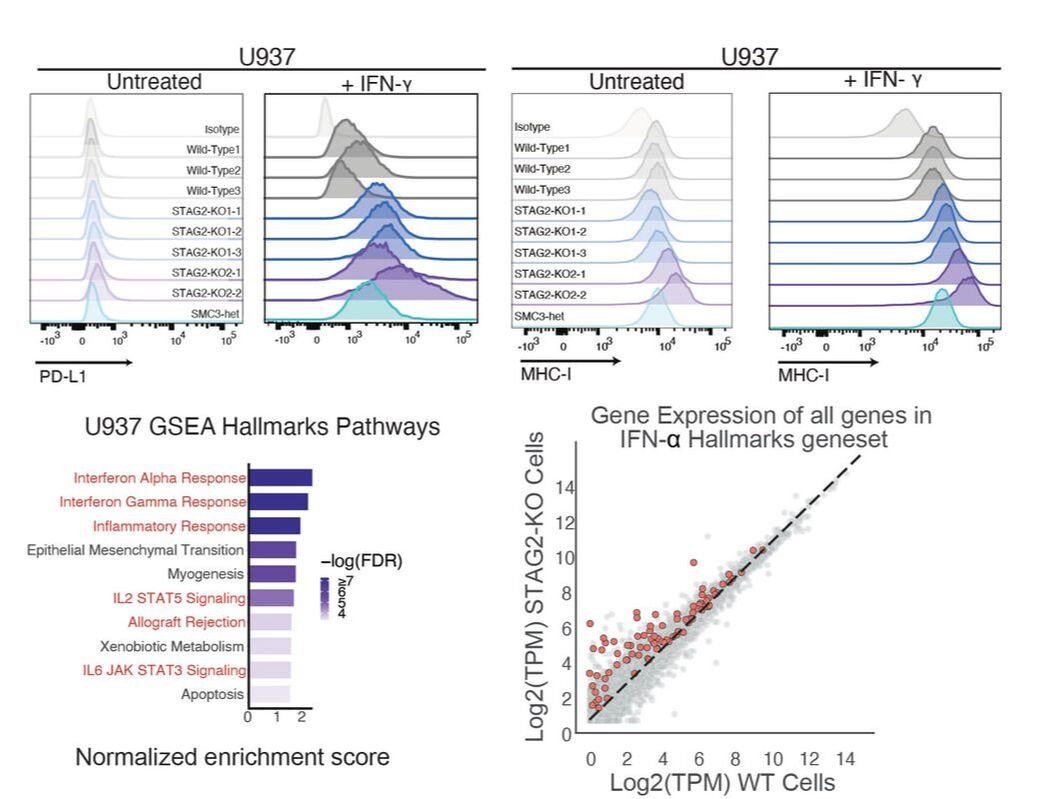
Genetic analysis of cancer drivers reveals cohesin and CTCF as suppressors of PD-L1.
PNAS. 2022 Feb 15; 119(7):e2120540119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2120540119. Immune evasion is a significant contributor to tumor evolution, and the immunoinhibitory axis PD-1/PD-L1 is a frequent mechanism employed to escape tumor immune surveillance. To identify cancer drivers involved in immune evasion, we performed a CRISPR-Cas9 screen of tumor suppressor genes regulating the basal and interferon (IFN)-inducible cell surface levels of PD-L1. Multiple regulators of PD-L1 were identified, including IRF2, ARID2, KMT2D, and AAMP. We also identified CTCF and the cohesin complex proteins, known regulators of chromatin architecture and transcription, among the most potent negative regulators of PD-L1 cell surface expression. Additionally, loss of the cohesin subunit RAD21 was shown to up-regulate PD-L2 and MHC-I surface expression. PD-L1 and MHC-I suppression by cohesin were shown to be conserved in mammary epithelial and myeloid cells. Comprehensive examination of the transcriptional effect of STAG2 deficiency in epithelial and myeloid cells revealed an activation of strong IFN and NF-κB expression signatures. Inhibition of JAK-STAT or NF-κB pathways did not result in rescue of PD-L1 up-regulation in RAD21-deficient cells, suggesting more complex or combinatorial mechanisms at play. Discovery of the PD-L1 and IFN up-regulation in cohesin-mutant cells expands our understanding of the biology of cohesin-deficient cells as well as molecular regulation of the PD-L1 molecule. |
Cohesin mutations in myeloid malignancies.Blood. 2021 June 22; blood.2019004259. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019004259. PMID: 34157074
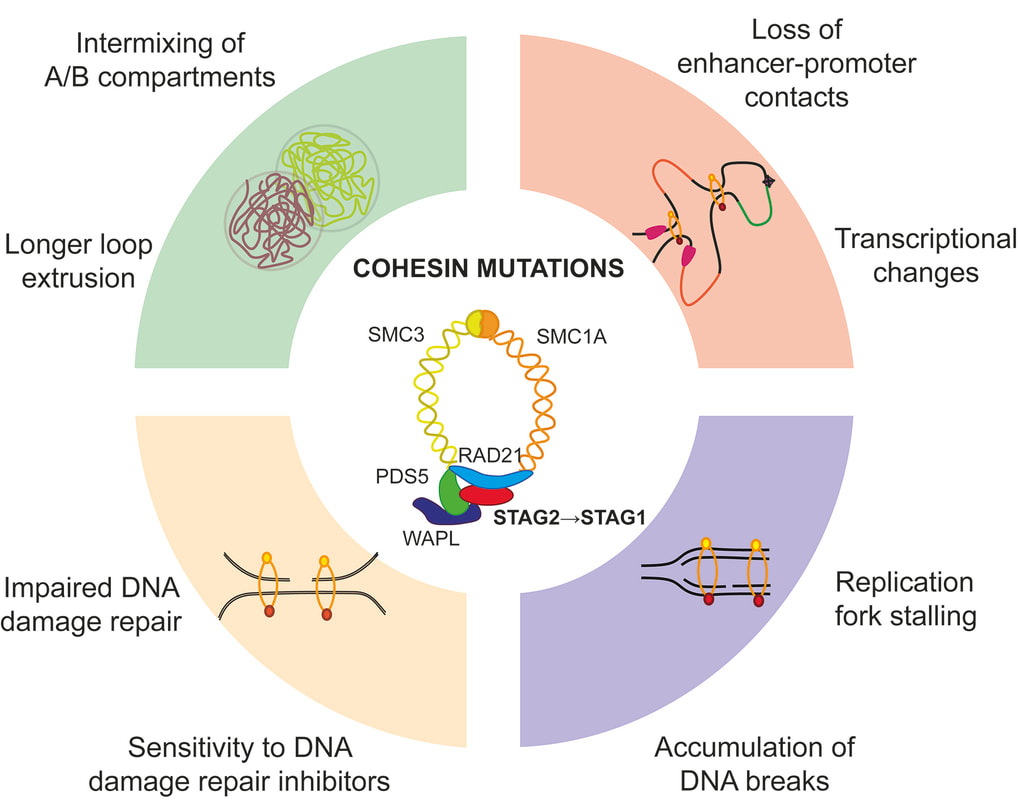
Cohesin is a multi-subunit protein complex that forms a ring-like structure around DNA. Cohesin is essential for sister chromatid cohesion, chromatin organization, transcriptional regulation and DNA damage repair, and plays a major role in dynamically shaping the genome architecture and maintaining DNA integrity. The core complex subunits STAG2, RAD21, SMC1 and SMC3, as well as its modulators PDS5A/B, WAPL and NIPBL, have been found to be recurrently mutated in hematologic and solid malignancies. These mutations are found across the full spectrum of myeloid neoplasia, including pediatric Down Syndrome-associated acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (DS-AMKL), myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), and de-novo and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The mechanisms by which cohesin mutations act as drivers of clonal expansion and disease progression are still poorly understood. Recent studies have described the impact of cohesin alterations on self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC), which are associated with changes in chromatin and epigenetic state directing lineage commitment, as well as genomic integrity. Here, we will review the role of the cohesin complex in healthy and malignant hematopoiesis. We will discuss clinical implications of cohesin mutations in myeloid malignancies and discuss opportunities for therapeutic targeting. |
Cohesin mutations alter DNA damage repair and chromatin structure and create therapeutic vulnerabilities in MDS/AML.JCI Insight. 2020 Dec 22;142149. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.142149. PMID: 33351783
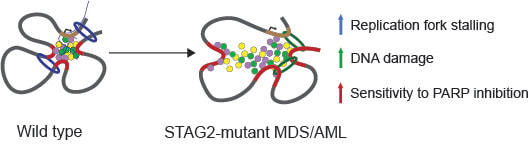
The cohesin complex plays an essential role in chromosome maintenance and transcriptional regulation. Recurrent somatic mutations in the cohesin complex are frequent genetic drivers in cancer including myelodysplatic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here, using genetic dependency screens of STAG2-mutant AML, we identified DNA damage repair and replication as genetic dependencies in cohesin-mutant cells. We demonstrated increased levels of DNA damage and sensitivity of cohesin-mutant cells to PARP inhibition. We developed a mouse model of MDS in which Stag2 mutations arise as clonal secondary lesions in the background of clonal hematopoiesis driven by Tet2 mutations, and demonstrated selective depletion of cohesin-mutant cells with PARP inhibition in vivo. Finally, we demonstrated a shift from STAG2- to STAG1-containing cohesin complexes in cohesin-mutant cells, which is associated with longer DNA loop extrusion, more intermixing of chromatin compartments, and increased interaction with PARP and RPA proteins. Our findings inform the biology and therapeutic opportunities for cohesin-mutant malignancies. |
Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome Editing in Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells Models Clonal Hematopoiesis and Myeloid Neoplasia.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Oct 5;21(4):547-555.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.07.015. PMID: 28985529
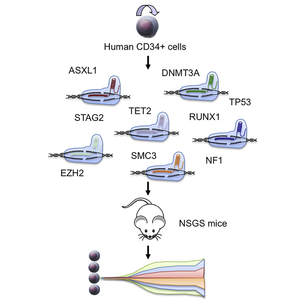
Hematologic malignancies are driven by combinations of genetic lesions that have been difficult to model in human cells. We used CRISPR/Cas9 genome engineering of primary adult and umbilical cord blood CD34 + human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), the cells of origin for myeloid pre-malignant and malignant diseases, followed by transplantation into immunodeficient mice to generate genetic models of clonal hematopoiesis and neoplasia. Human hematopoietic cells bearing mutations in combinations of genes, including cohesin complex genes, observed in myeloid malignancies generated immunophenotypically defined neoplastic clones capable of long-term, multi-lineage reconstitution and serial transplantation. Employing these models to investigate therapeutic efficacy, we found that TET2 and cohesin-mutated hematopoietic cells were sensitive to azacitidine treatment. These findings demonstrate the potential for generating genetically defined models of human myeloid diseases, and they are suitable for examining the biological consequences of somatic mutations and the testing of therapeutic agents. To view all of our publications, please click here
|
Photo credits: Francisco Marty, MD and Rebecca Gorelov, BA